Skill development
This tutorial demonstrates how to develop and use custom skills through two examples: first creating a weather reporting skill from scratch, and then using that skill to generate weather comparisons and visualizations.
Prerequisites
It is recommended to complete the Basic Usage tutorial before proceeding with this one, as it covers fundamental concepts that are built upon here.
Interactive development
This section demonstrates the interactive development of a custom weather reporting skill through a conversation between a user and a freeact agent. You'll see how the agent assists with software engineering tasks, evolving a simple weather query into a Python package that can:
- Fetch current weather conditions for any city
- Resolve city names to geographical coordinates
- Retrieve historical weather data
- Return structured data for both current and historical weather
The development progresses through several iterations:
- Creating a code action to fetch Vienna's weather
- Converting it into a proper Python package
- Adding city name coordinate resolution
- Incorporating historical weather data
- Testing with various cities (New York, Vienna, Salzburg)
The interactively developed weather.weather_report skill uses the Open-Meteo API for weather data and geocoding.
Note
Interactive skill development is currently only supported for Claude models.
The example conversation below was initiated with the following freeact.cli command1. The developed weather.weather_report skill is written to the workspace/skills/private/example directory.
python -m freeact.cli \
--model-name=anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 \
--ipybox-tag=ghcr.io/gradion-ai/ipybox:example \
--executor-key=example \
--skill-modules=freeact_skills.search.google.stream.api \
--skill-modules=freeact_skills.zotero.api \
--skill-modules=freeact_skills.reader.api
Example conversation
Skill usage
This section demonstrates how to use the previously developed weather reporting skill in a separate conversation. After loading weather.weather_report as additional skill2, we'll see how the agent can:
- Create multi-city weather reports with much smaller code actions
- Create data visualizations comparing weather patterns
- Provide clear, natural language summaries of weather conditions
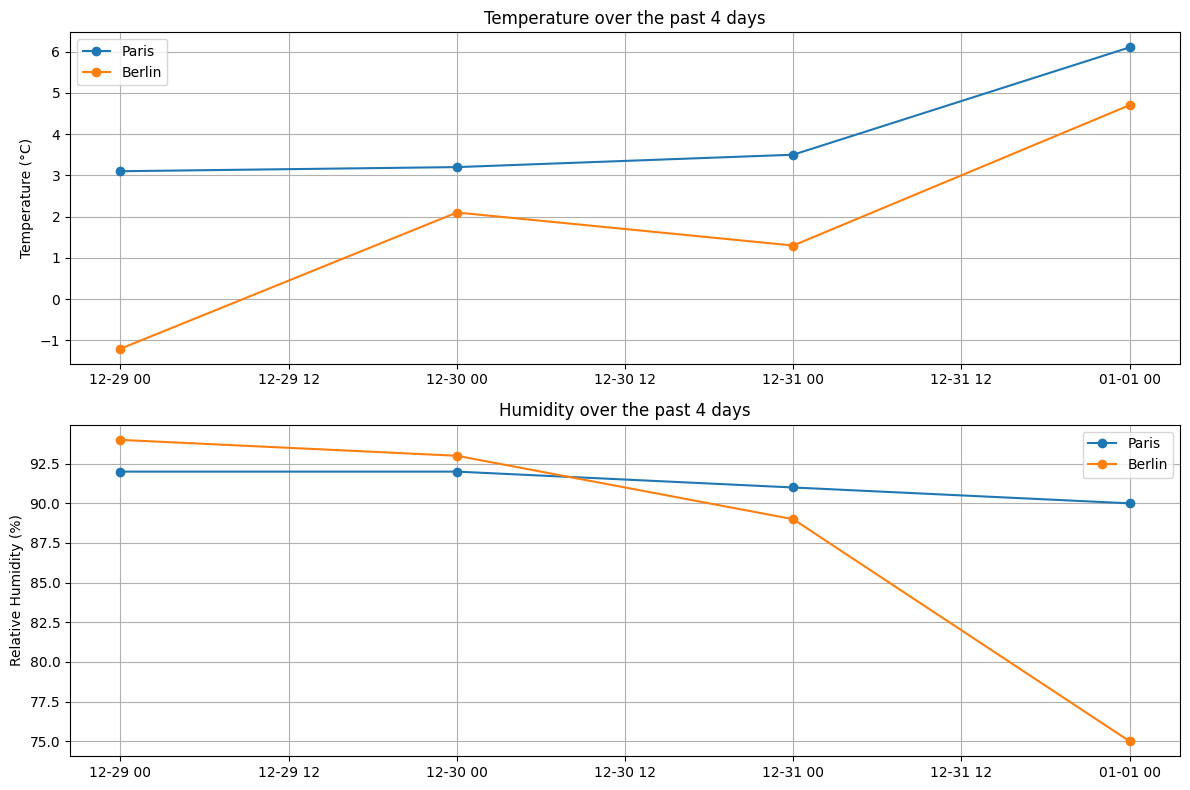
The example shows a request for weather data from Paris and Berlin, where the agent automatically:
- Retrieves current conditions and 4-day history for both cities using the
weather.weather_reportskill - Creates comparative visualizations of temperature and humidity trends
- Presents the data in both graphical and text formats
The example conversation was initiated with the following freeact.cli command. The developed skill is is read from workspace/skills/private/example. If we moved it to workspace/skills/shared, it would be available to all executors regardless of their executor-key value.
python -m freeact.cli \
--model-name=anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 \
--ipybox-tag=ghcr.io/gradion-ai/ipybox:example \
--executor-key=example \
--skill-modules=freeact_skills.search.google.stream.api \
--skill-modules=freeact_skills.zotero.api \
--skill-modules=freeact_skills.reader.api \
--skill-modules=weather.weather_report
Note
If you've developed a custom skill that has external dependencies, you either need to build a custom Docker image with the required dependencies or need to install them at runtime prior to launching an agent.
Example conversation
Produced images: